Decision tree models are a type of supervised machine learning algorithm used for classification and regression tasks. They work by recursively splitting the data into subsets based on feature values, creating a tree-like structure where each internal node represents a feature, each branch represents a decision rule, and each leaf node represents an outcome or class label.
Dataset¶
Our dataset,
| Outlook | Temperature | Humidity | Windy | Play |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| sunny | hot | high | false | no |
| sunny | hot | high | true | no |
| overcast | hot | high | false | yes |
| rainy | mild | high | false | yes |
| rainy | cool | normal | false | yes |
| rainy | cool | normal | true | no |
| overcast | cool | normal | true | yes |
| sunny | mild | high | false | no |
| sunny | cool | normal | false | yes |
| rainy | mild | normal | false | yes |
| sunny | mild | normal | true | yes |
| overcast | mild | high | true | yes |
| overcast | hot | normal | false | yes |
| rainy | mild | high | true | no |
Code¶
dataset = [
['sunny', 'hot', 'high', 'false', 'no'],
['sunny', 'hot', 'high', 'true', 'no'],
['overcast', 'hot', 'high', 'false', 'yes'],
['rainy', 'mild', 'high', 'false', 'yes'],
['rainy', 'cool', 'normal', 'false', 'yes'],
['rainy', 'cool', 'normal', 'true', 'no'],
['overcast', 'cool', 'normal', 'true', 'yes'],
['sunny', 'mild', 'high', 'false', 'no'],
['sunny', 'cool', 'normal', 'false', 'yes'],
['rainy', 'mild', 'normal', 'false', 'yes'],
['sunny', 'mild', 'normal', 'true', 'yes'],
['overcast', 'mild', 'high', 'true', 'yes'],
['overcast', 'hot', 'normal', 'false', 'yes'],
['rainy', 'mild', 'high', 'true', 'no']
]import pandas as pd
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier, plot_tree
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, classification_report, confusion_matrix
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = [row[:-1] for row in dataset]
y = [row[-1] for row in dataset]
x = pd.DataFrame(x, columns=['outlook', 'temperature', 'humidity', 'windy'])
y = pd.Series(y)
le = LabelEncoder()
for column in x.columns:
x[column] = le.fit_transform(x[column])
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=42)
clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion='entropy')
clf = clf.fit(x_train, y_train)
accuracy = clf.score(x_test, y_test)
print(f'Accuracy: {accuracy * 100:.2f}%')Accuracy: 60.00%
test_data = pd.DataFrame([['sunny', 'cool', 'high', 'true']], columns=['outlook', 'temperature', 'humidity', 'windy'])
for i in test_data.columns:
test_data[i] = le.fit_transform(test_data[i])
clf.predict(test_data)array(['yes'], dtype=object)Plot¶
class_report = classification_report(y_test, clf.predict(x_test))
print('Classification Report:')
print(class_report)Classification Report:
precision recall f1-score support
no 0.50 0.50 0.50 2
yes 0.67 0.67 0.67 3
accuracy 0.60 5
macro avg 0.58 0.58 0.58 5
weighted avg 0.60 0.60 0.60 5
conf_mat = confusion_matrix(y_test, clf.predict(x_test))
print('Confusion Matrix:')
print(conf_mat)Confusion Matrix:
[[1 1]
[1 2]]
plt.figure(figsize=(10,20))
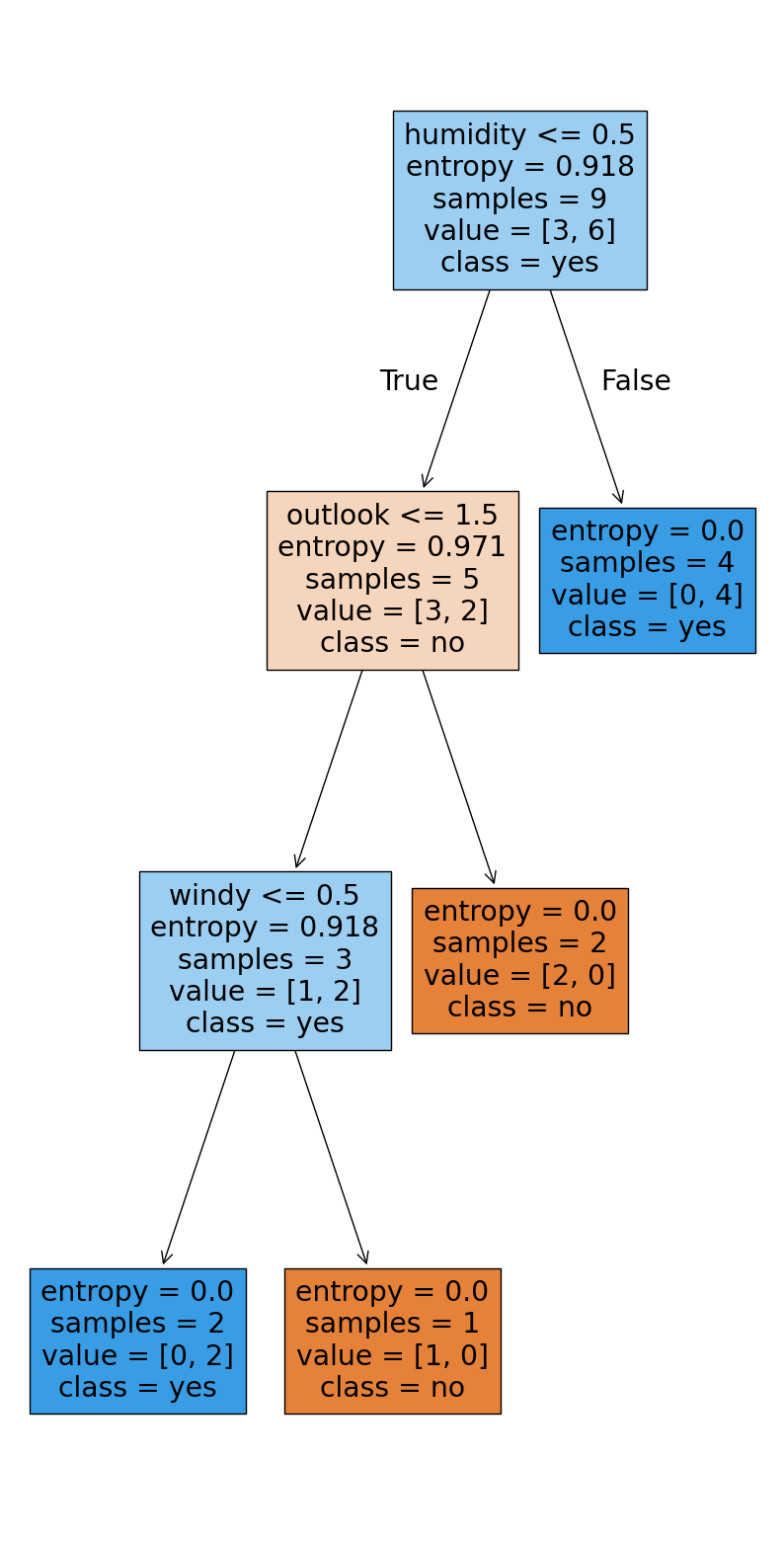
plot_tree(clf, feature_names=x.columns, class_names=clf.classes_, filled=True)[Text(0.6666666666666666, 0.875, 'humidity <= 0.5\nentropy = 0.918\nsamples = 9\nvalue = [3, 6]\nclass = yes'),
Text(0.5, 0.625, 'outlook <= 1.5\nentropy = 0.971\nsamples = 5\nvalue = [3, 2]\nclass = no'),
Text(0.5833333333333333, 0.75, 'True '),
Text(0.3333333333333333, 0.375, 'windy <= 0.5\nentropy = 0.918\nsamples = 3\nvalue = [1, 2]\nclass = yes'),
Text(0.16666666666666666, 0.125, 'entropy = 0.0\nsamples = 2\nvalue = [0, 2]\nclass = yes'),
Text(0.5, 0.125, 'entropy = 0.0\nsamples = 1\nvalue = [1, 0]\nclass = no'),
Text(0.6666666666666666, 0.375, 'entropy = 0.0\nsamples = 2\nvalue = [2, 0]\nclass = no'),
Text(0.8333333333333334, 0.625, 'entropy = 0.0\nsamples = 4\nvalue = [0, 4]\nclass = yes'),
Text(0.75, 0.75, ' False')]